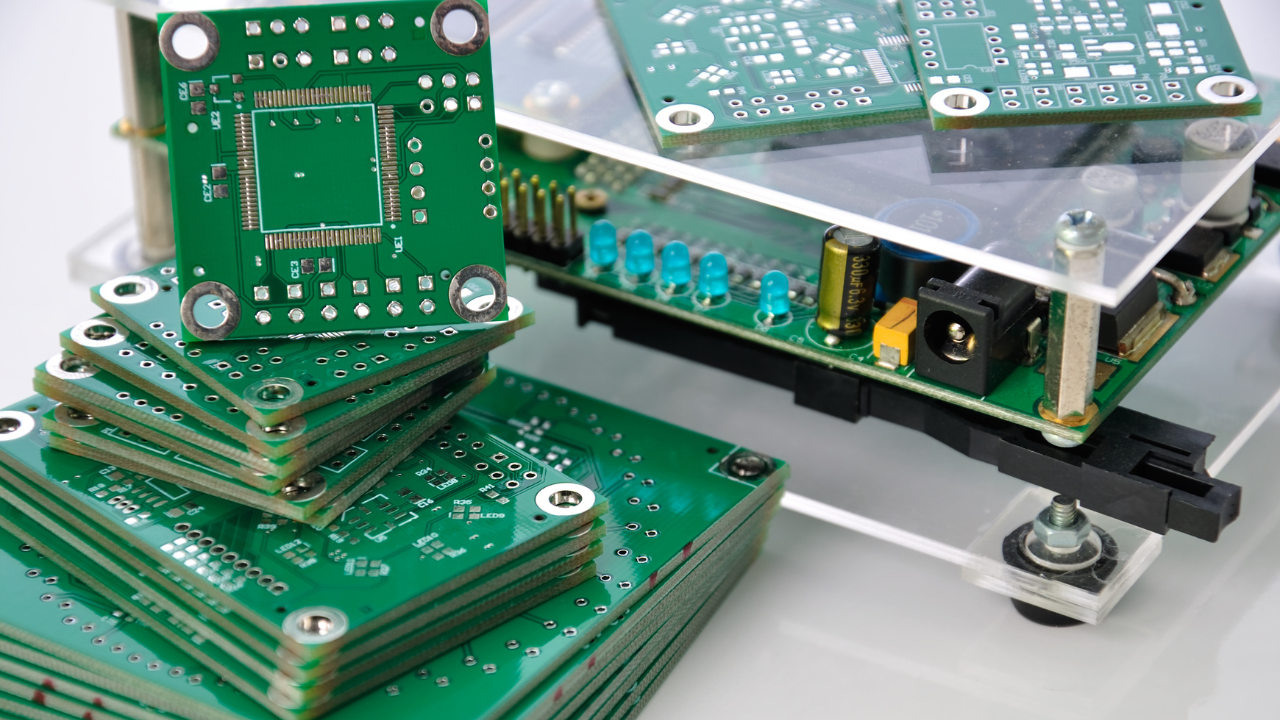
A PCB, or printed circuit board, prototype is a crucial step in the design and development of electronic devices. A prototype allows engineers and designers to test the functionality and performance of a circuit before it is mass-produced thus reducing the overall cost of the project and increasing the chance of success.. In this article, we will discuss the stages of developing a PCB prototype and the benefits it provides.
An Overview of PCB Prototyping: The Stages
It is not uncommon to produce multiple prototypes throughout the process to allow for testing and optimizations, Some of these test may include:
- Electrical testing: This includes testing for proper power and signal integrity, as well as checking for any shorts or open circuits on the board.
- Functional testing: This tests to see if the prototype performs the specific functions it is designed for.
- Thermal testing: This test is to evaluate if the prototype can operate correctly under different temperatures and conditions, checking how well the device is able to dissipate heat and if it can operate within the expected temperature range.
- EMI (Electromagnetic interference) testing: This test is to evaluate how well the prototype is able to function in the presence of electromagnetic interference and to ensure it meets regulatory compliance.
- Reliability testing: This test evaluates how well the prototype withstands different conditions over time and if it will last for the expected lifespan.
- Environmental testing: This test is to evaluate how well the prototype is able to function under different environmental conditions, such as vibration, shock, humidity, and temperature.
- Mechanical testing: This test is to evaluate the strength and robustness of the physical components of the prototype, such as the connections between the PCB and the components.
- Compliance testing: This test is to check if the prototype meets any industry standards or regulations.
Testing can occur at any phase and may be completed multiple times throughout the prototyping process. Below outlines the stages of development:
A Proof of Concept Prototype
A proof-of-concept prototype focuses on replicating the primary function of the board without all of the bells and whistles that the final product will have. The goal of this prototype is to show that the overall purpose of the PCB is viable. Once the proof-of-concept prototype has passed its tests, a visual model can be mocked up.
A Visual Model
A visual model is one of the earliest prototypes used during the design process. This can be done using computer-aided design (CAD) software, such as Altium Designer, Eagle, or KiCAD. The design file, usually in Gerber format, is then sent to a PCB fabrication company for production. The overall goal of this prototype is to show that the PCB is not only viable but also affordable. The individual components, structures. and the shape of the final PCB will be the focus of this prototype.
A Working Prototype
A working prototype is one of the later stages in the design process. A working PCB prototype is a functional board that has all of the intended functions and features of the PCB itself. Using this prototype, it is possible to identify errors or mistakes in the design that need to be rectified before the rest of the production moves forward. It is not unusual to have significant changes between the working prototype and the final product.
A Functional Prototype
A functional prototype is a PCB prototype that is as close to the finished product as possible. The goal is to provide a crystal-clear idea of what the final PCB will look like, how it will work, and the exact materials that will be used. Some finishing touches might be applied to the functional prototype in an effort to get the cost down, but the final PCB will look similar to the functional prototype.
It is not unusual for engineers to produce every prototype on the list as they design a printed circuit board. If you work with a quality team, they will keep you updated as the process unfolds, letting you know how the prototype process is proceeding. They might also provide you with some updates on the overall cost of the project as you make changes to the design along the way.
Ready to get started? Request a quote today!
What Are the Top Benefits of PCB Prototyping?
The prototyping process is incredibly important to the overall design of your printed circuit boards. Some of the biggest benefits of PCB prototyping include:
1. Saves Time: You want to get your order as quickly as possible, but you also want to receive high-quality printed circuit boards. If you want to save time during the design process, PCB prototyping is essential. Some of the reasons why the prototyping process can help you save time include:
- Your entire PCB will be tested from top to bottom. This gives the team an opportunity to spot problems before they work their way through your entire order.
- With a comprehensive prototyping process, revisions will be reduced. Instead of making changes to the entire order, changes can be made to the prototype before the rest of the chips are produced properly on the first attempt.
- If you want to see your PCBs as the design process unfolds, prototypes are beneficial. That way, when the engineers explain something to you, you will have a visual model in front of you, allowing you to understand exactly what is being discussed.
2. Saves Money: The PCB prototyping process can also help you save money along the way. Even though you might get frustrated as changes are made to the design, these changes will help you save money in the long run.
If changes aren’t made to the design when problems are discovered, these problems will work your way through all of your PCBs. Then, you will have a finished order, but a lot of chips that don’t work properly. You will have to go through and make changes to each individual chip, which will cost a significant amount of money.
Furthermore, during the testing process, the engineers may realize that less expensive materials can deliver the same outcome. These material switches can be monumental in the long haul.
3. Improve the Final Design of the PCB: Finally, prototyping can help you improve the final design and performance of the PCB. For example…
- The prototyping process can test individual components made from different materials to figure out which ones work best for your needs.
- PCB prototyping can also help you test different types of design theories, helping to find the best design theory that works well for your chip.
- The individual functions of complex designs can be tested on their own merits. That way, engineers can figure out how to get each function to work with each component in perfect harmony.
Work With Imagineering To Manufacture Your Next PCB, Starting With Prototyping
Starting with a PCB prototype is a crucial step in the design and development of electronic devices. It allows for early identification and correction of any issues, testing and optimization of the design, and validation of the end use requirements.
At Imagineering, we will walk you through the prototyping process, provide expert recommendations along the way and leverage our equipment and team of experts to quickly and efficiently assemble your PCB prototypes.
As a result, it can ultimately save time and money in the long run, and lead to a higher-performing and more cost-effective final product. Contact us today to get started!