Even the most well-crafted devices won’t last forever. Electronic parts, such as PCBs, suffer wear and tear over time, eventually requiring repair or replacement for the device’s overall health.
However, it’s not always possible to replace your old devices. You also may not want to fork over hundreds of or thousands of dollars to have your device professionally repaired.
Luckily, there are many ways to help maintain your PCBs and repair them on your own.
Simple problems you can fix on your own include intermittent loss of power, overheating, non-responsive components, physical damage (including corrosion), and broken circuits.
In this guide, we’ll introduce some basic troubleshooting techniques, a breakdown of what tools and supplies you’ll need to repair your PCBs, and cover some circumstances in which it might be best to turn to a professional.
Importance of Maintaining Healthy PCBs
Defects or damage to your PCB can lead to erratic behavior, intermittent failures, or complete device malfunctions.
A faulty PCB can sometimes pose a safety risk, such as overheating or electrical hazards.
Learning to repair or replace PCBs on your own can be a challenge, but squashing minor issues before they become major problems can minimize downtime, prevent damage to other components, and extend the overall lifespan of your devices.
5 Signs Your PCB May Need Repair or Replacement
Here are five signs that your PCBs could malfunction due to damage or faults, as well as some tips on how to repair the PCB.
1. Intermittent or Total Loss of Power
Start by identifying the cause of the loss of power, which may or may not be connected to the PCB.
Troubleshooting Power Issues
- Verify that the power source is functioning properly and that the cable and connections are not damaged.
- Check the solder joints for loose or broken connections, especially around power input/output areas. Look closely at power-related components like fuses, voltage regulators, and diodes.
- Use a multimeter to check the continuity of traces between components—it may be necessary to perform a PCB trace repair to reopen a damaged circuit.
Repair/Replacement for Power Issues
- Repairing loose connections can be as simple as carefully resoldering the joint or repairing the trace.
- If multiple components are damaged, or the issue is too difficult to identify, consider replacing the PCB entirely.
2. Overheating or Burn Marks on the PCB
A lack of proper ventilation or exposure to high temperatures from other device components can cause overheating. Short circuits can also cause excessive current flow and overheating, especially heat-sensitive parts like capacitors, resistors, and diodes.
Preventive Measures and Cooling Solutions
Ensure your PCB can access proper ventilation and airflow to prevent overheating. Consider the device’s overall design to facilitate the flow of cool air over the PCB.
Perform a visual check, or use a multimeter, to ensure no accidental connections between traces or components that might lead to short circuits.
If you notice extensive burn damage, damage to multiple parts, or can’t determine the cause of the overheating, it may be best to replace the PCB.
3. Malfunctioning or Non-Responsive Components
You may notice that certain features of your device are not working as intended, which may be due to malfunctioning or unresponsive components on your PCB.
Detecting Malfunctioning Components
- Use a multimeter to test the function of individual components.
- Inspect connections to ensure all components are secure and properly soldered.
- Check for damaged or broken traces on the PCB.
Importance of Proper Soldering and Component Installation
Improperly soldered components can cause many problems for your PCB, such as:
- Electrical connectivity issues (including open and short circuits).
- Cold joints lead to weak bonds and intermittent connections.
- Solder splatter and flux residue.
- Reflow issues can be caused by improper reflow soldering surface-mount technology (SMT). You may notice some components lifting off the PCB due to uneven heating.
4. Visible Physical Damage or Corrosion
Cracks, chips, and bent components can be signs of permanent damage to your PCB.
- Apart from obvious physical defects like cracks or chips, look for more subtle signs of corrosion, discoloration, or moisture damage. Look for greenish or white deposits around components or traces.
- Focus visual inspections on different board parts and review them multiple times. Start with each component, then look at solder joints, traces, and circuits. Breaking down the inspection process will make it easier to spot and make note of each issue.
- You can subject your PCB to light pressure or gentle bending (if applicable) to see if any components are shifting or breaking due to weak connections.
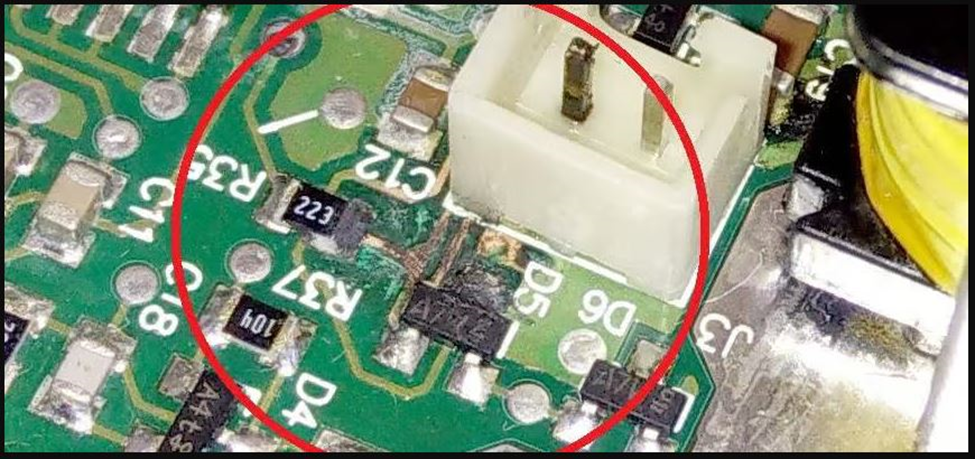
Dealing with Corrosion and Environmental Damage
Physically damaged components can be desoldered and replaced with new ones.
Some corrosion can be cleaned with isopropyl alcohol or a specialized cleaning solution. However, if the corrosion is extensive or widespread, you should consider replacing the entire PCB.
5. Frequent Circuit Shortages or Open Circuits
You may notice your device is unstable, unpredictable, or malfunctioning during regular use. This may be because of circuit shortages on the PCB.
Diagnosing Short and Open Circuits
- The easiest way to check for shorted or open circuits is to use a multimeter—an open circuit will show infinite resistance, while a closed circuit will display low resistance.
- Look for unintentional connections between adjacent traces or components.
- Examine the PCB for any trace discontinuities.
PCB Troubleshooting and PCB Repair Techniques
When encountering issues with your PCB (Printed Circuit Board), following a structured troubleshooting approach can help you identify and resolve problems effectively. Here’s a step-by-step guide to troubleshoot your PCB:
- Inspect: Begin by collecting as much information as possible about the issue you’re facing. You should also conduct a thorough visual inspection of the PCB looking for signs of physical damage, such as burnt components, disconnected traces, or damaged solder joints.
- Multimeter Diagnostics: Utilize a digital multimeter (DMM) to perform various tests:
- Voltage Checks: Measure voltages at critical points to verify if they match the expected values.
- Resistance Checks: Test the resistance of components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors to ensure they are within their specified ranges.
- Continuity Checks: Check for continuity between different points on the PCB to identify broken traces or open connections.
- Conduct Additional Test: You may conduct other testing to troubleshoot the issue including:
- Temperature Tests
- Signal Tracing
- Software and Firmware Updates
- Environmental Factors
- Seek Professional Help: After documenting your findings, and resolving any known problems, you should consider reaching out to professional PCB repair services or your PCB manufacturer for expert assistance.
Remember that PCB troubleshooting requires patience and methodical exploration. By following these steps, you’ll increase your chances of successfully diagnosing and resolving issues with your PCB.
Let Imagineering Manufacture and Assemble your PCBs
Remember that the best way to avoid costly or time-consuming repairs is to source your PCBs and components from the highest-quality manufacturers.
If you’ve designed your PCB and are looking for a professional one-stop shop that can manufacture and assemble it, Imagineering is here to help. Since 1986, we’ve combined aerospace-standard manufacturing and assembly with quick turnaround and a passion for serving our clients.
Whether you’re a small-scale hobbyist or a professional designer with a cutting-edge idea that you hope to turn into a reality, Imagineering has the tools and expertise to help you make your vision real.To start working with our team, get in touch and request a quote today.
FAQ About PCB Repair:
Can I Repair a PCB with Multiple Issues?
It’s possible to repair a PCB that has multiple issues. However, depending on the scope and extent of the damage, it may be more cost-effective to replace the PCB or the entire device simply.
How Do I Know If a Component Needs Replacement?
Diagnosing problems is generally a multi-step process that involves visual inspections and the use of digital tools like a multimeter or oscilloscope.
Should I Replace or Upgrade an Older PCB?
It may make sense to replace it simply depending on how old or degraded the PCB is. Consider factors like performance, longevity, part availability, and cost-effectiveness to determine if repairing or replacing your PCB makes more sense.


